There are 7.25 billion people living on the planet, and more than half of the world’s population has been living in cities since 2008. According to the Population Division of the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, the world’s urban population will grow to 6.4 billion by 2050. Each city is struggling to deal with this issue by developing new high-density residential areas such as satellite cities. However, urban sprawl is not the only solution.
93-99 PARK LANE, LONDON, UK
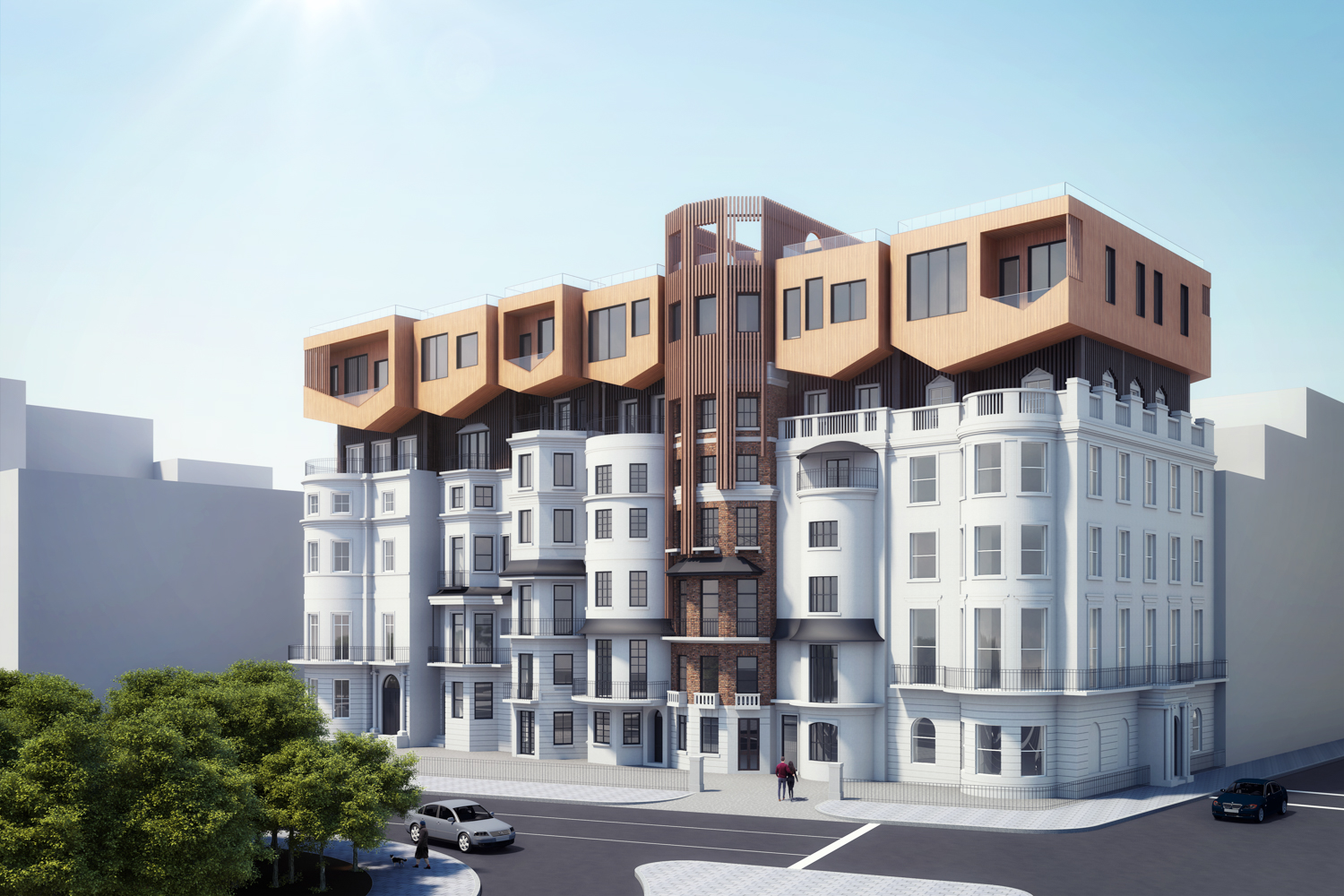
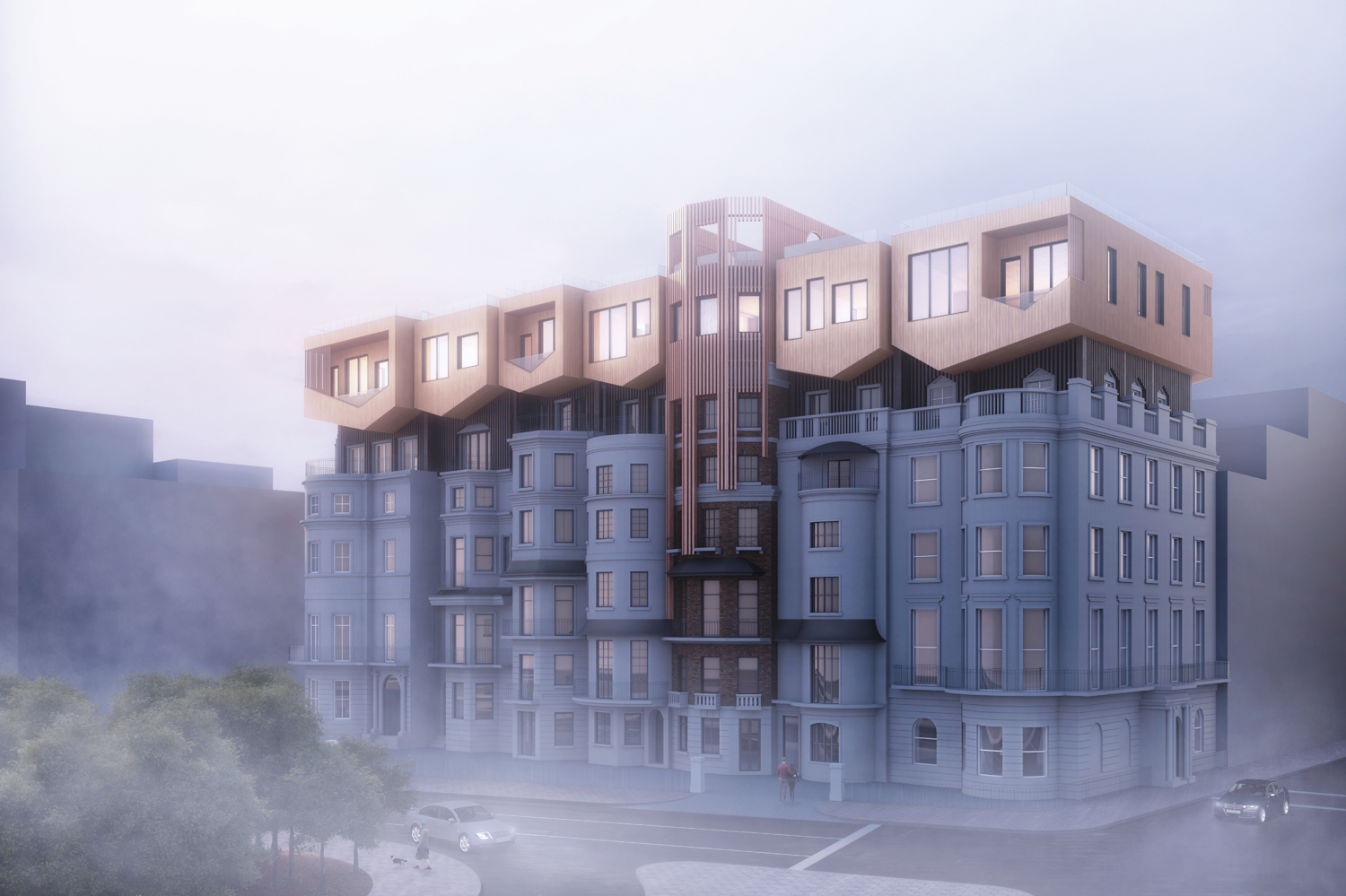
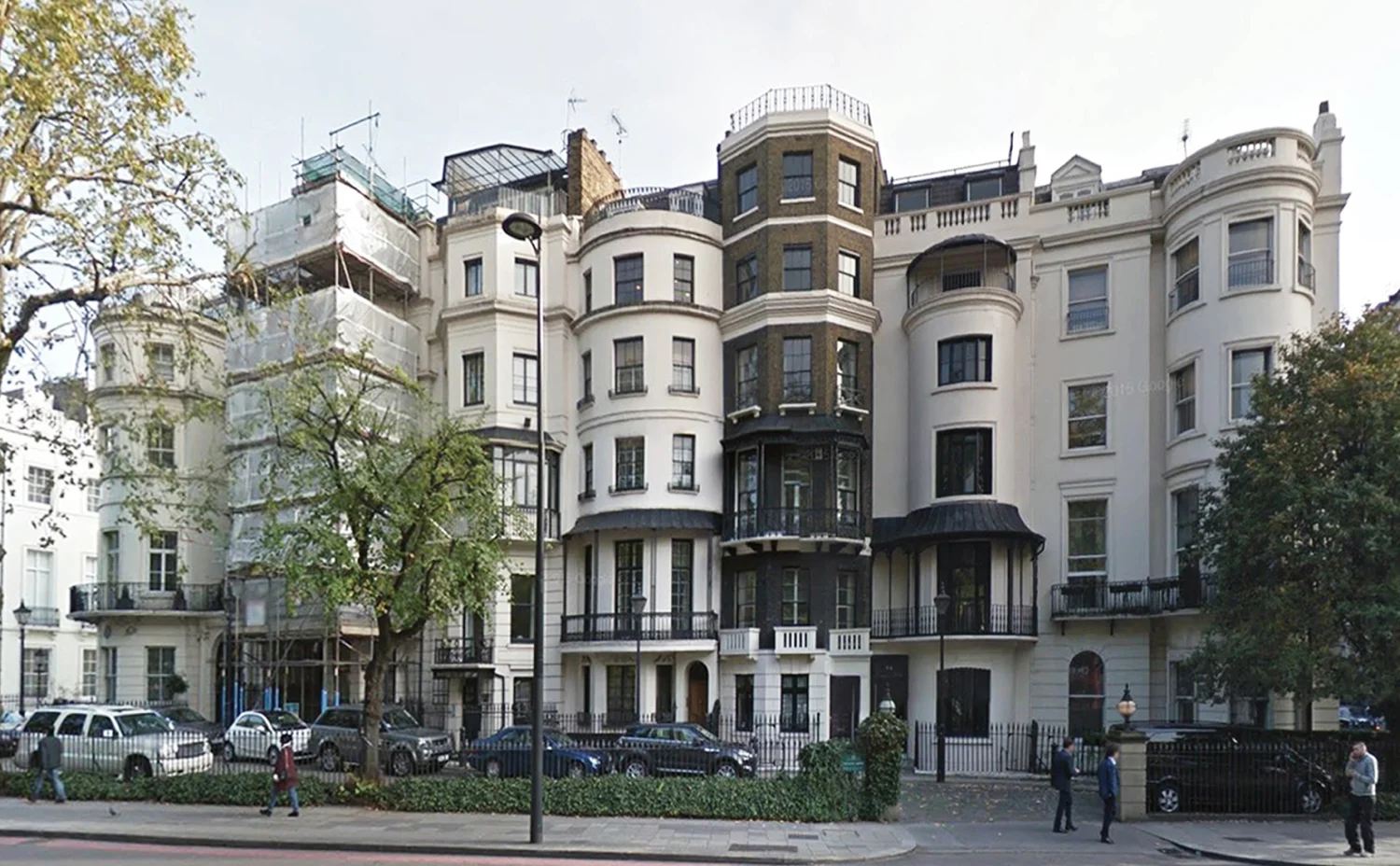
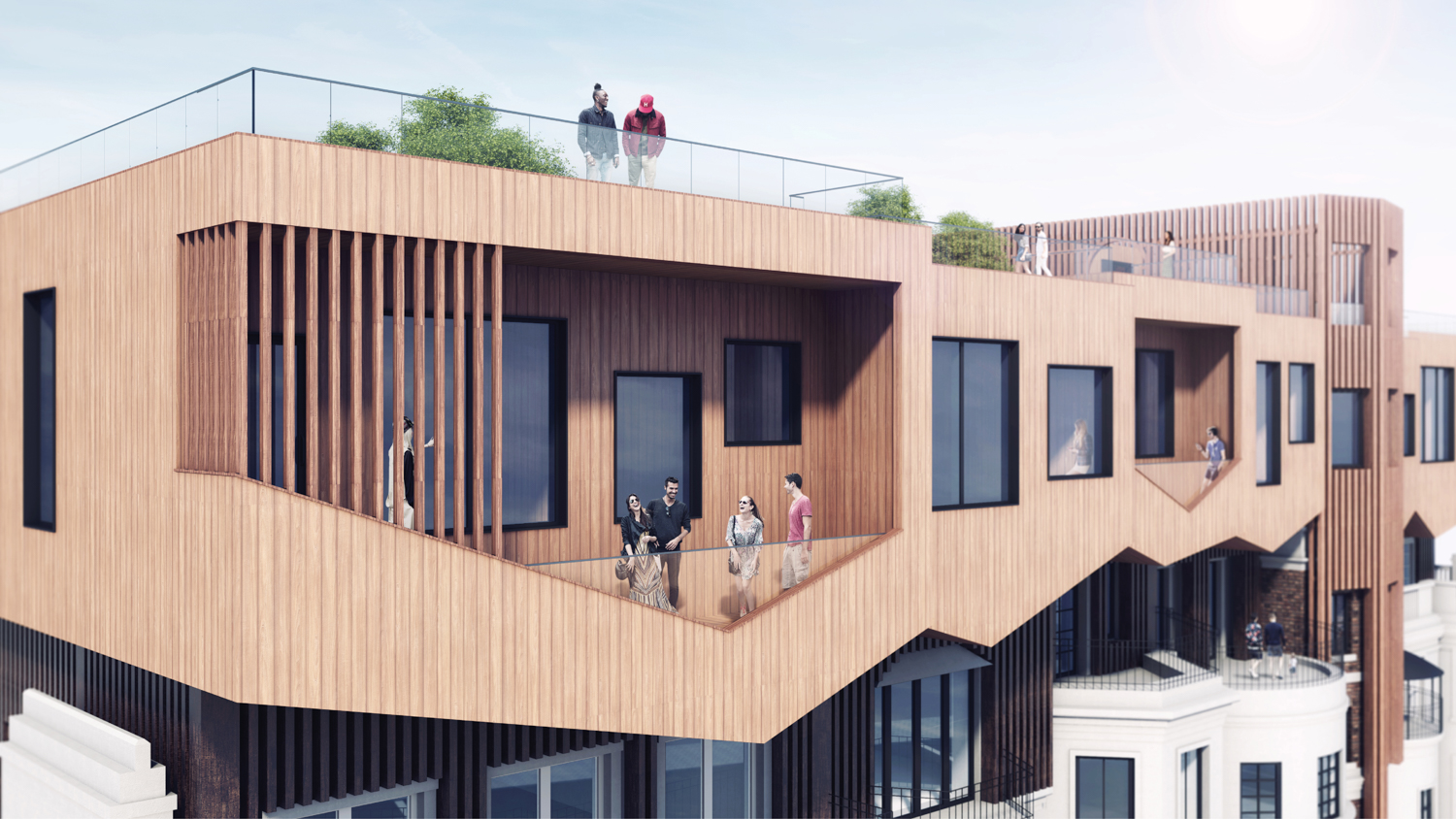
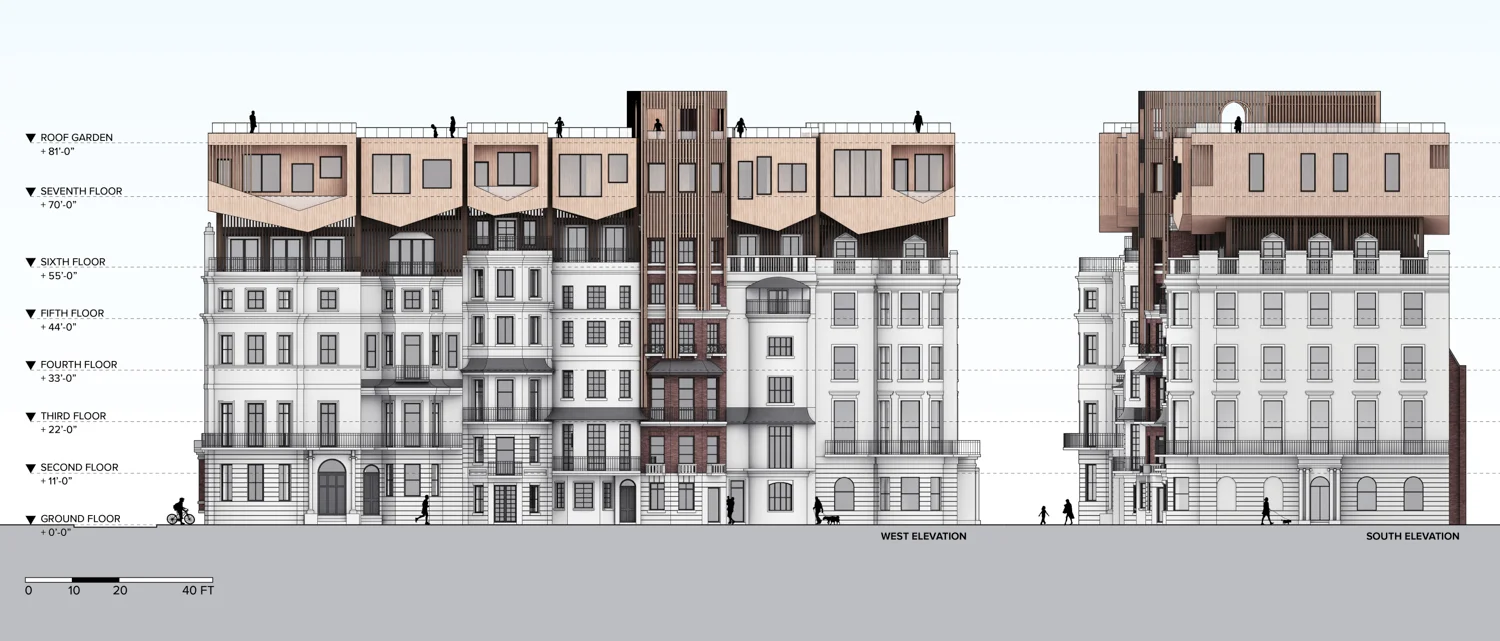
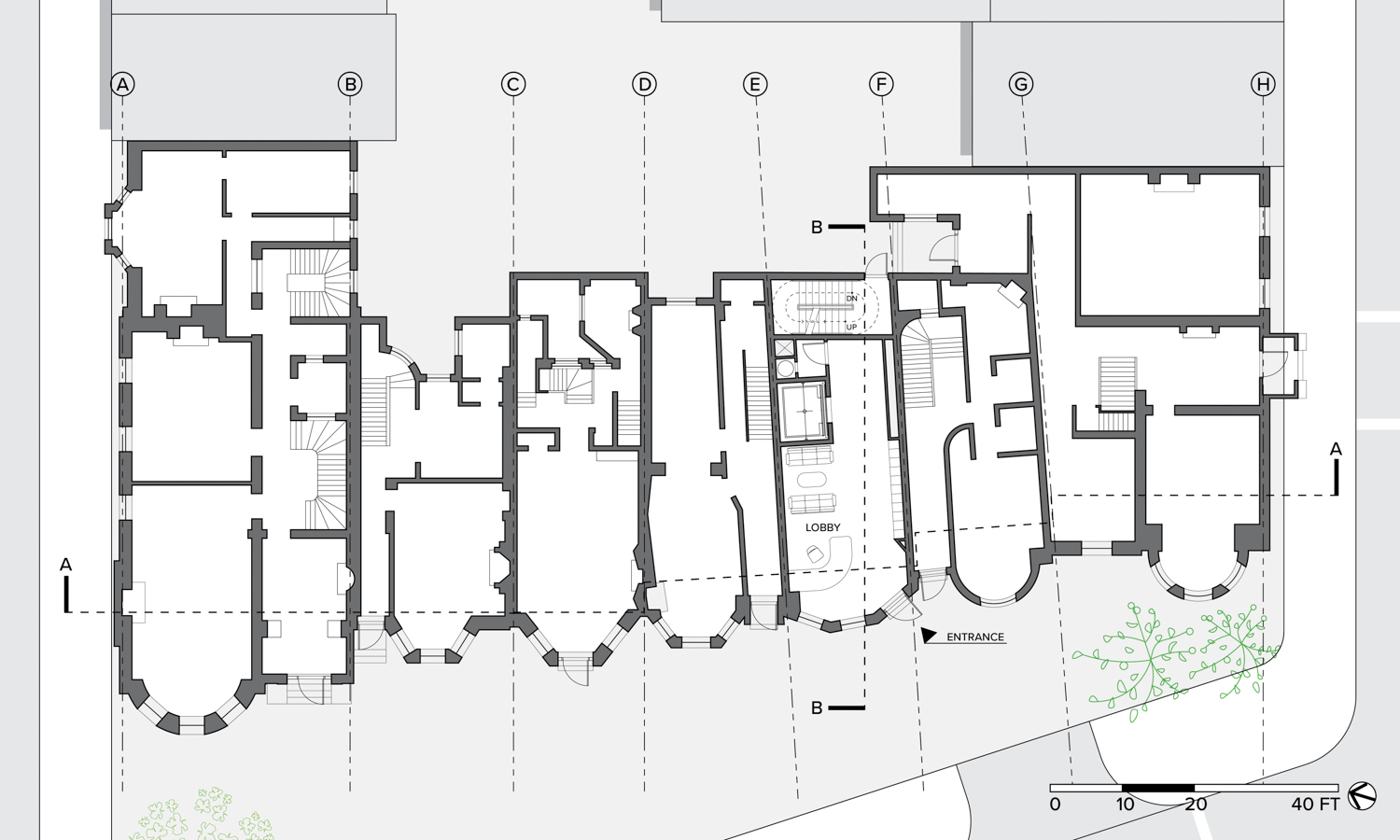
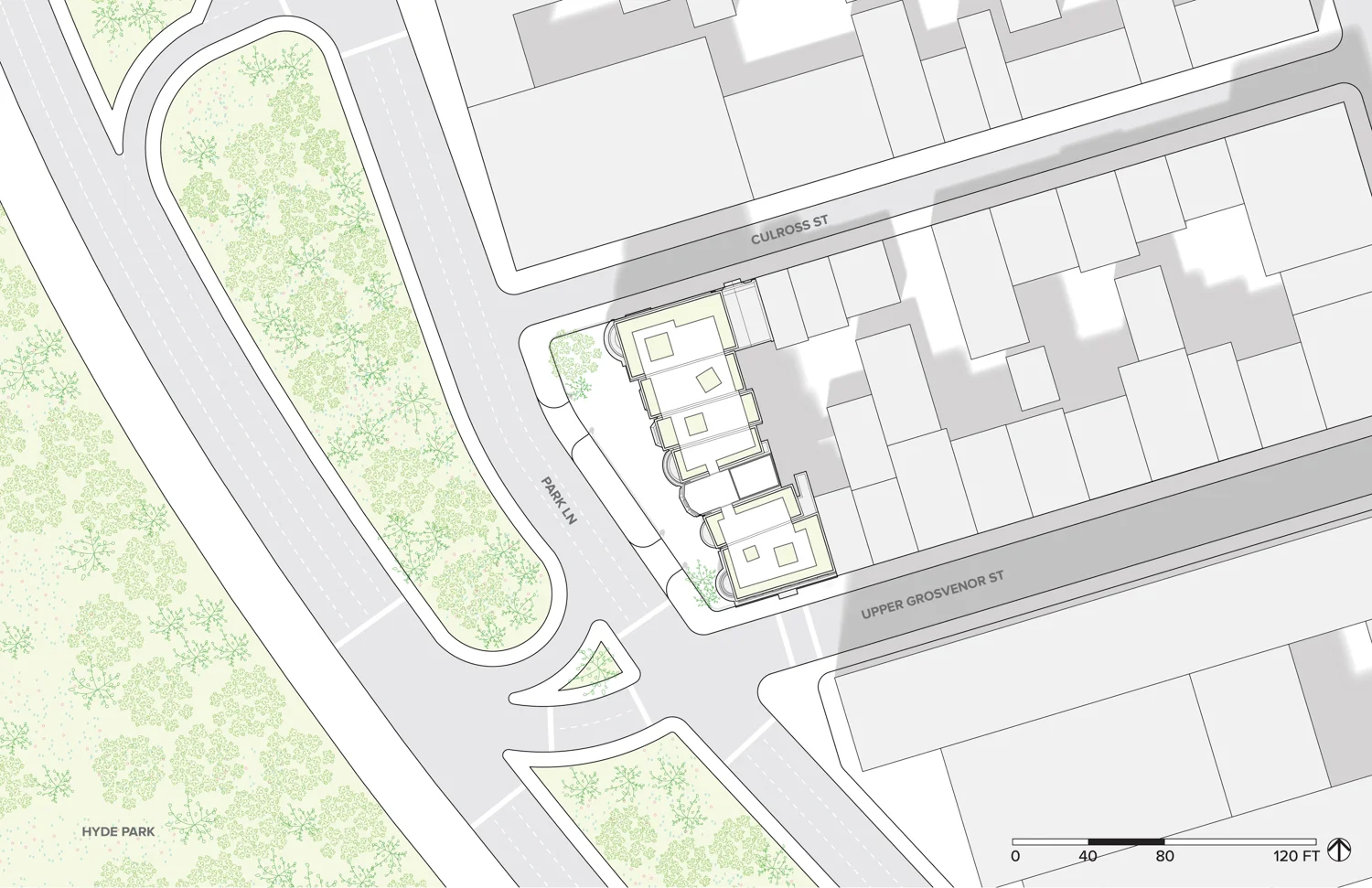
The site is located in Mayfair in London’s West End, toward the east edge of Hyde Park. The buildings were erected in the early 19th century between Upper Grosvenor Street and Culross Street. A row of seven houses offers a great view over Hyde Park. The district is mixed with commercial and residential property as well as upmarket shops and a restaurant. The neighborhood, one of the most expensive pieces of real estate in London is also well preserved. In this district, renovation is preferred to building new houses after demolishing old ones because of the original buildings’ historical features and real estate value. Therefore, Mayfair is a good location to test design solutions by creating additional floor areas.
ROW HOUSE
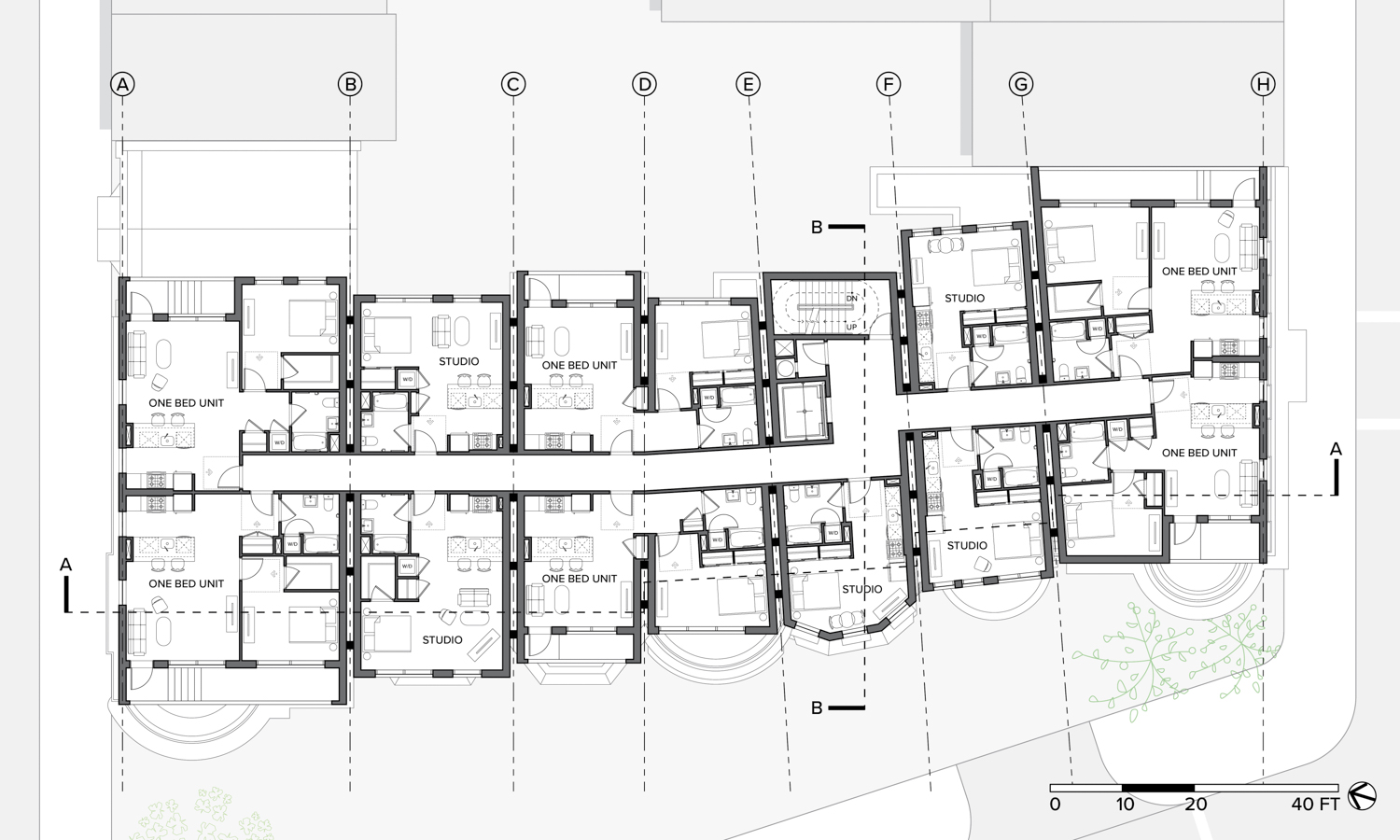
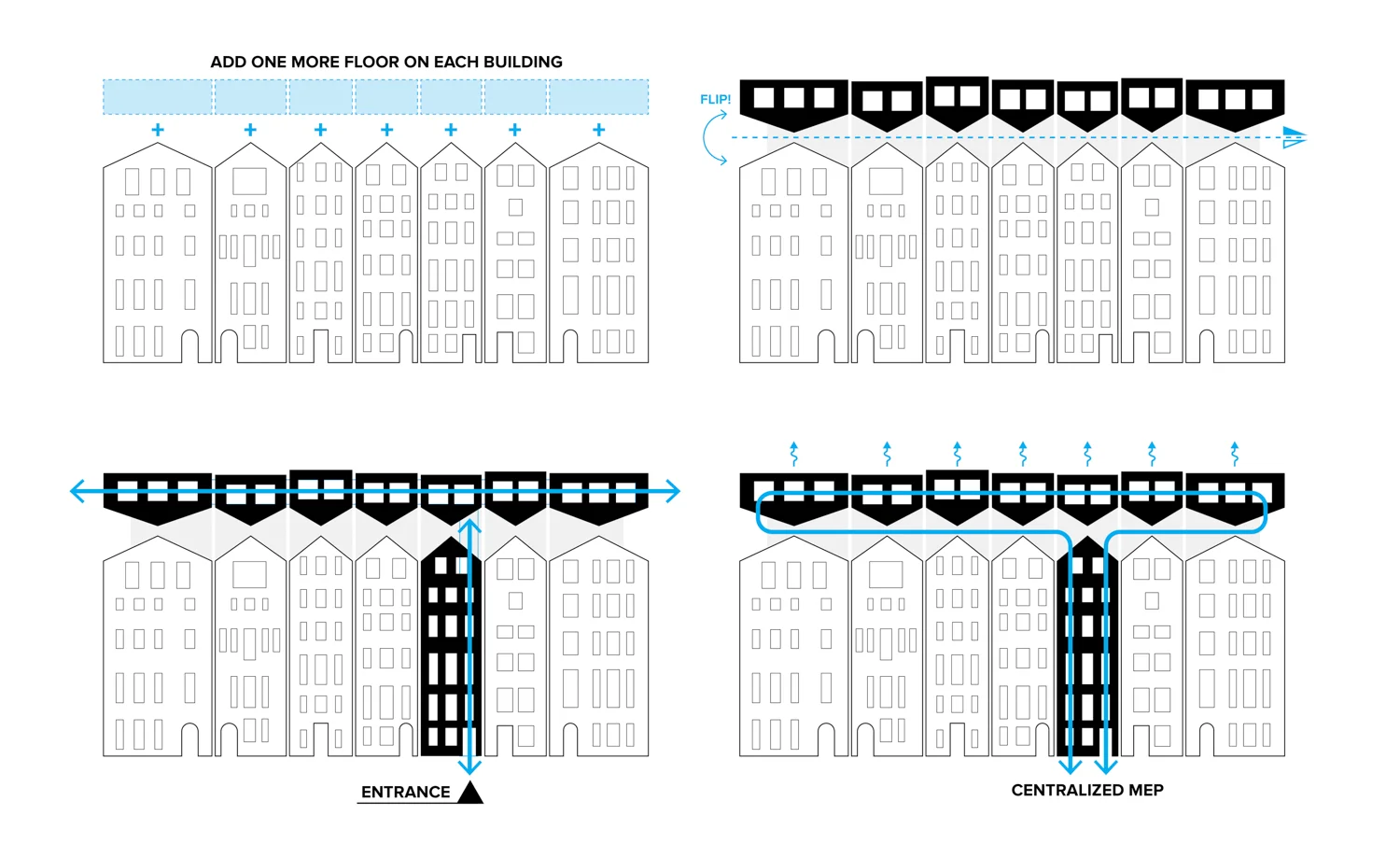
Row houses have been popular in Western countries since the 16th century. These are known as terrace houses and they are one of the most dominant architectural elements in the existing urban fabric of old cities such as London, Paris, and New York. Because of their historical value, redeployment is not easy, and there is the concern that such redeployment will destroy the fabric of existing cities. Adding another floor upon an existing row house will be one solution for dealing with urban sprawl and preserving urban fabric. This is also an environmentally friendly and economical approach. A typical row house has four or five floors. According to the research, one additional wooden structure floor can be added on the top of the buildings.
DESIGN APPROACH
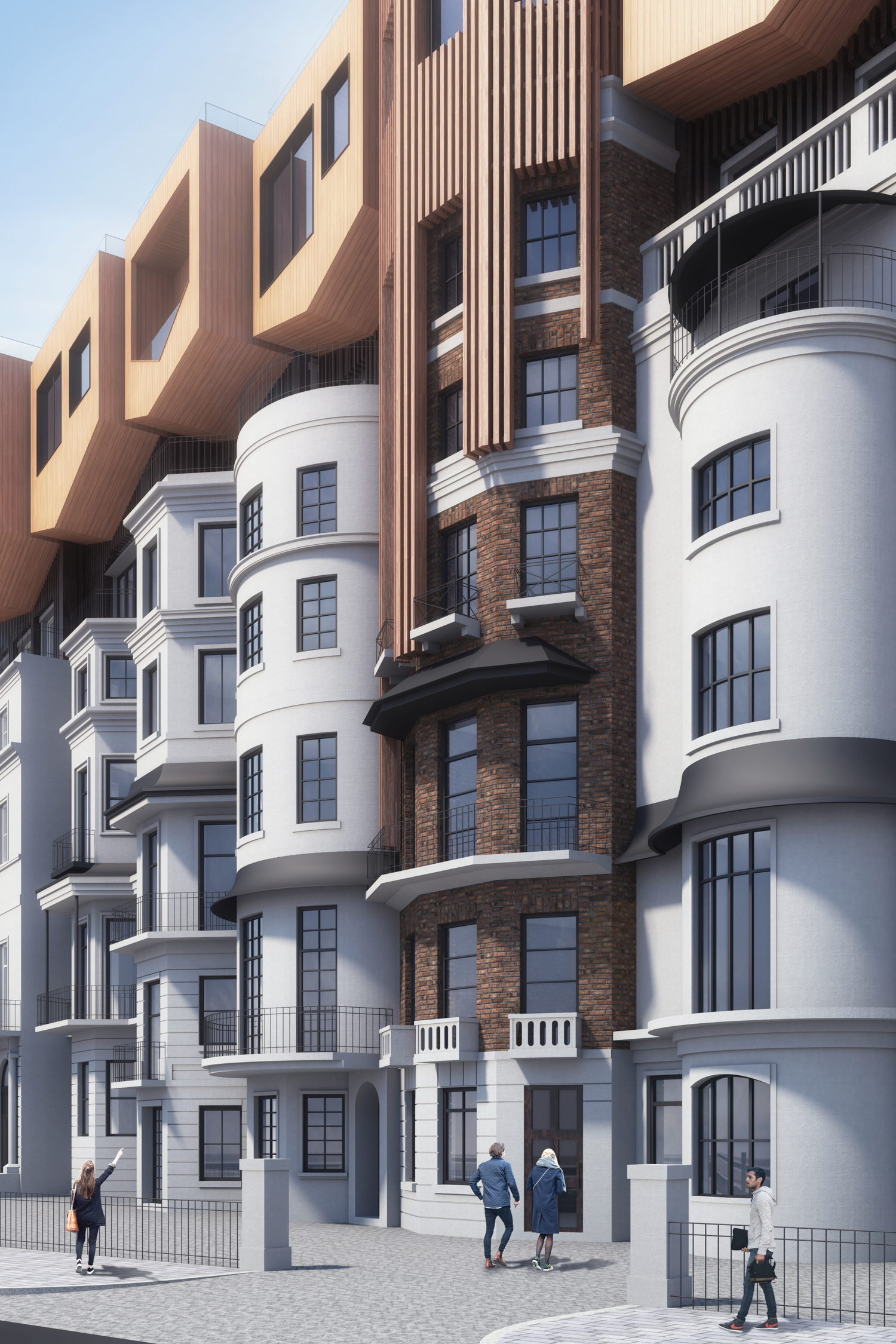
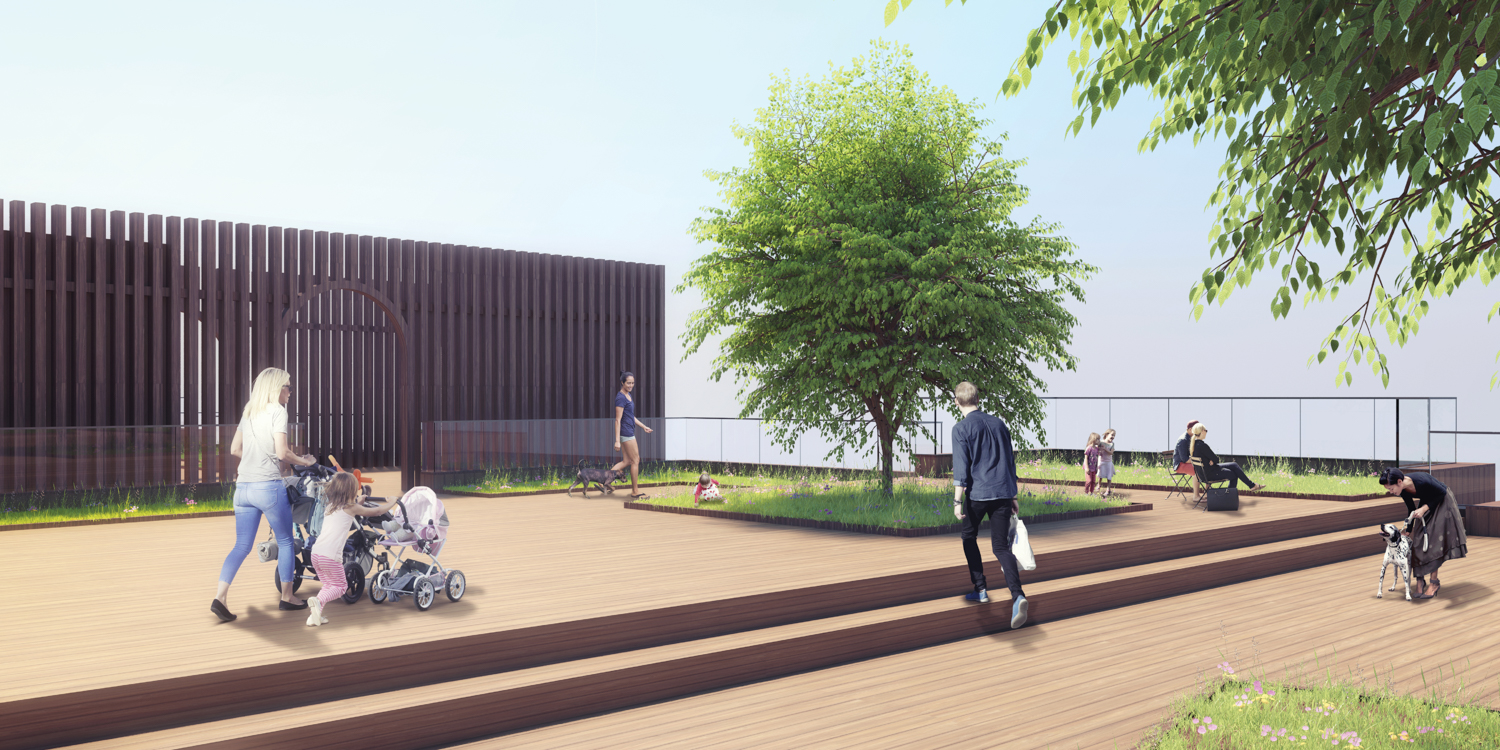
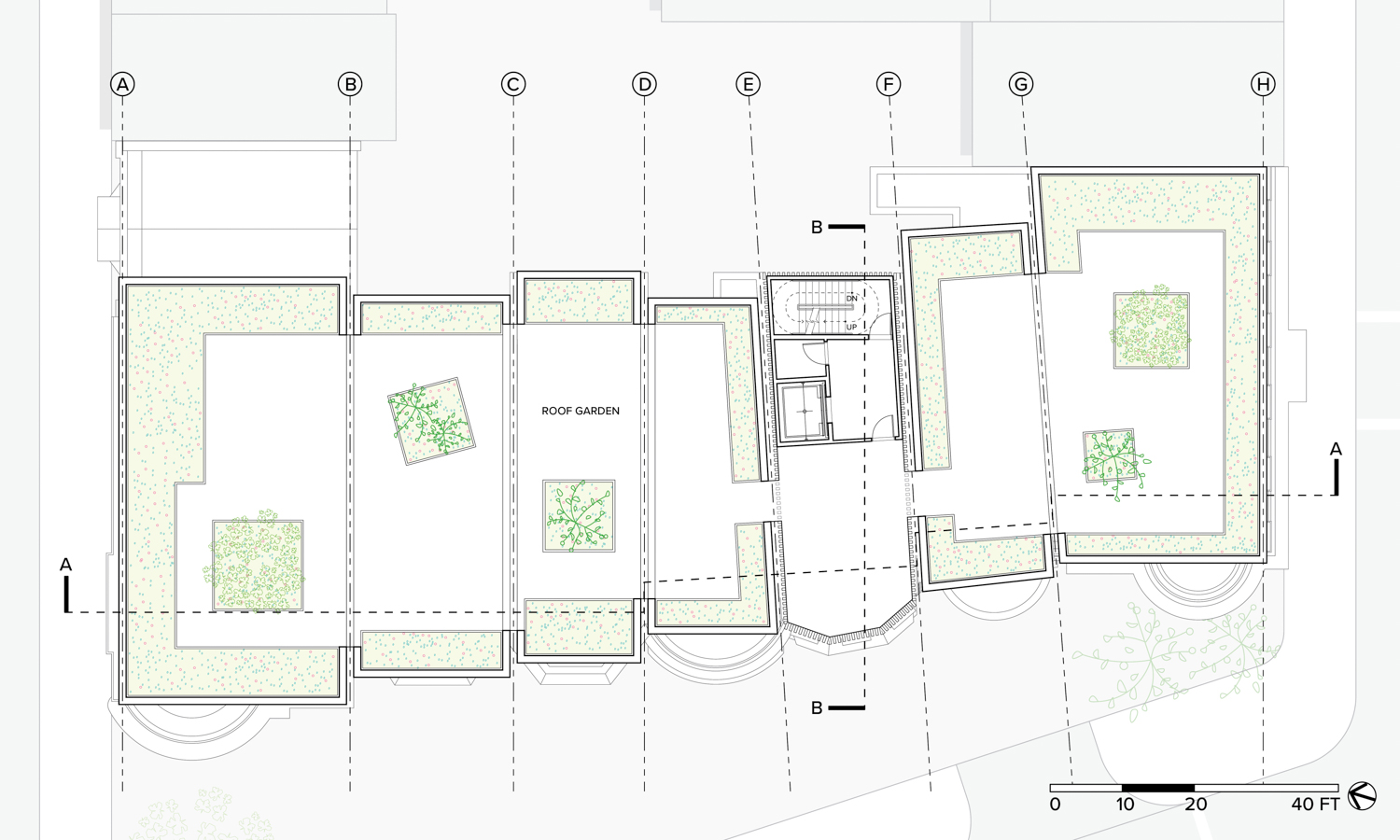
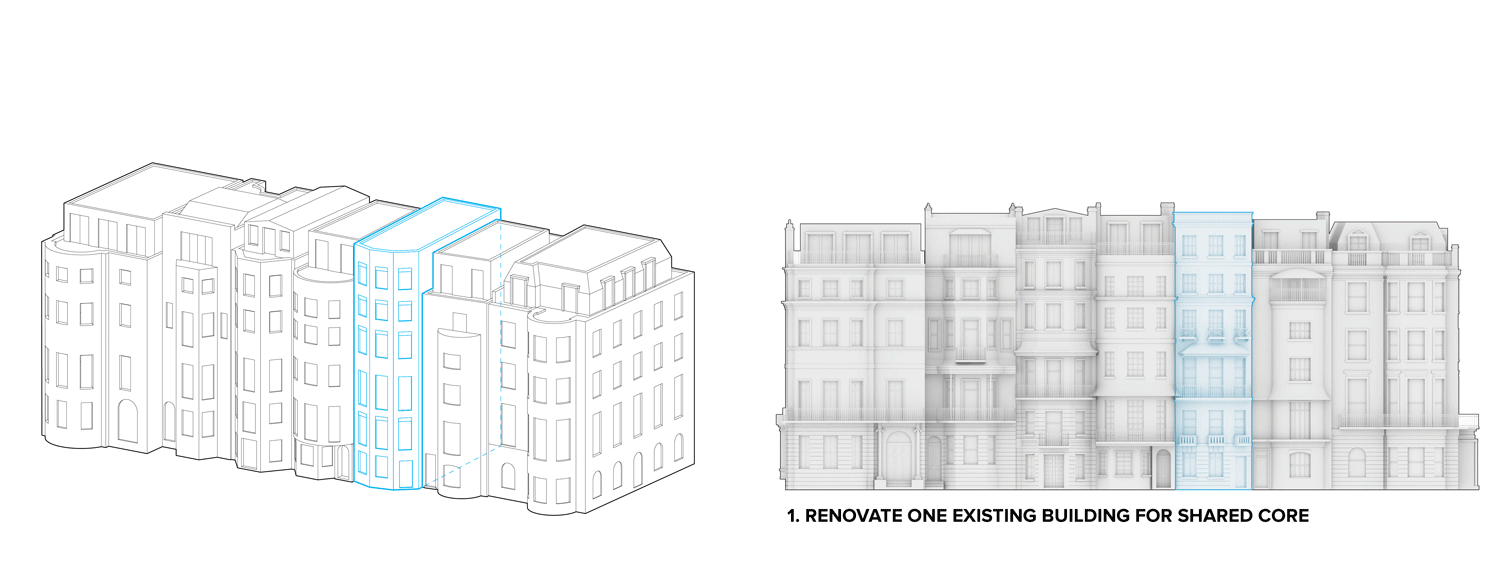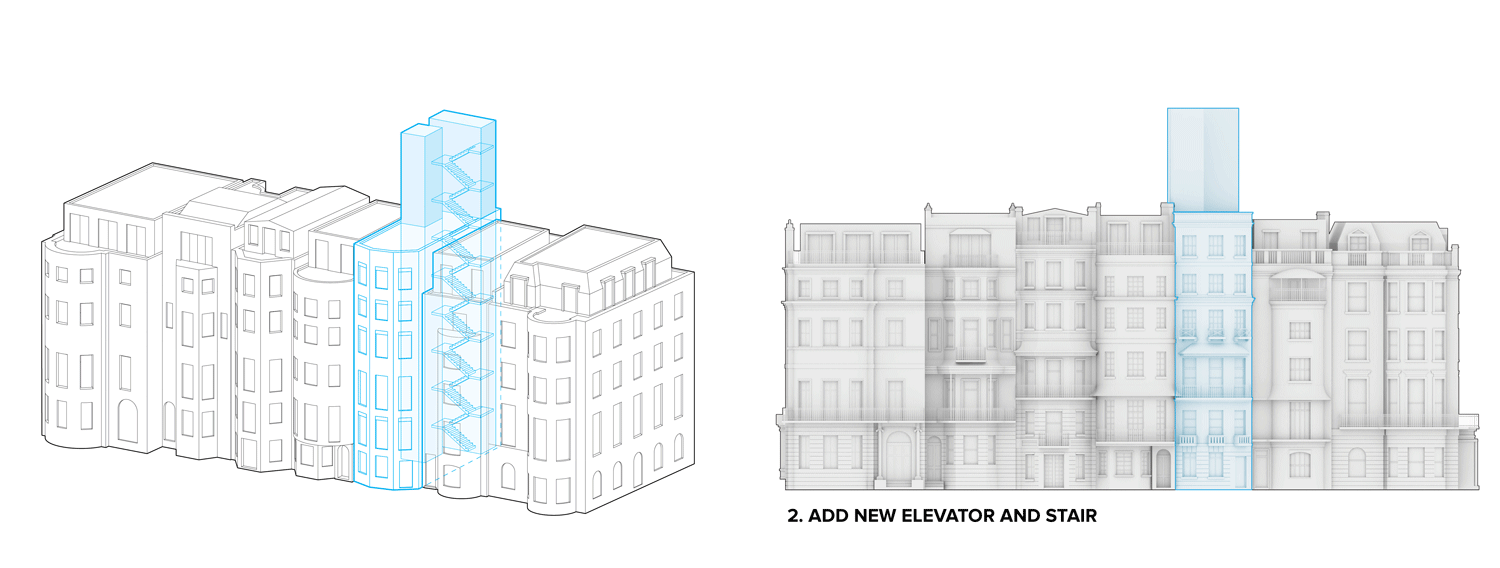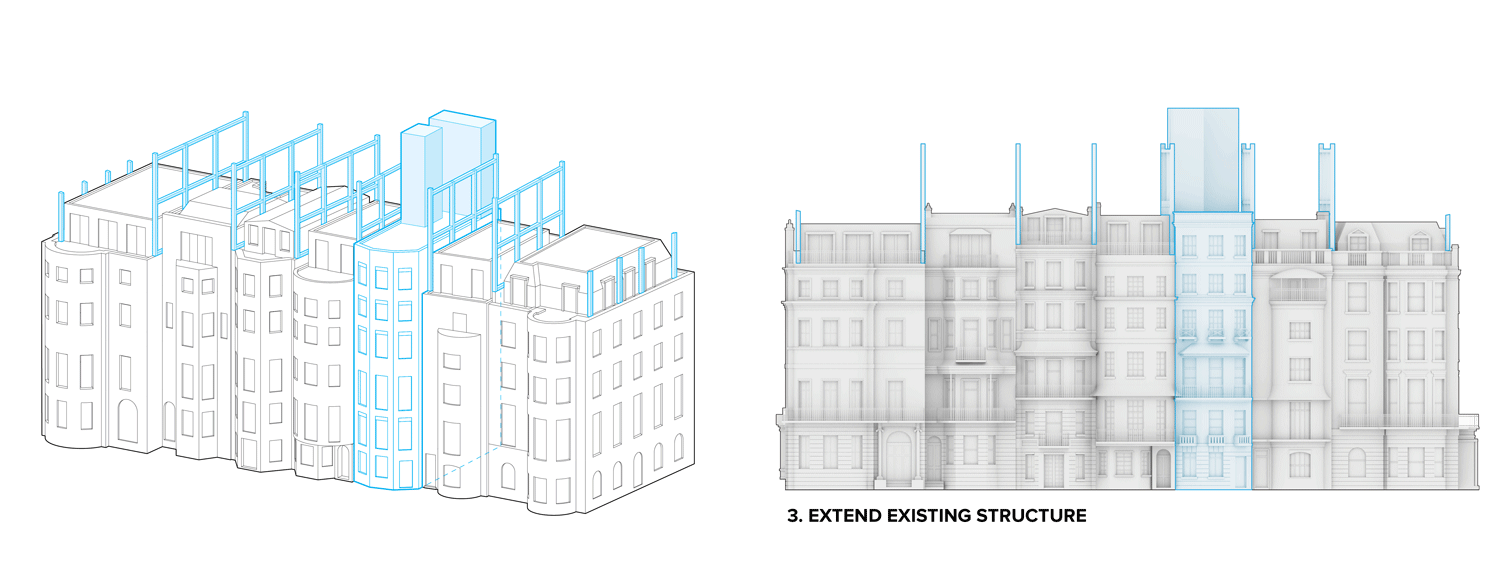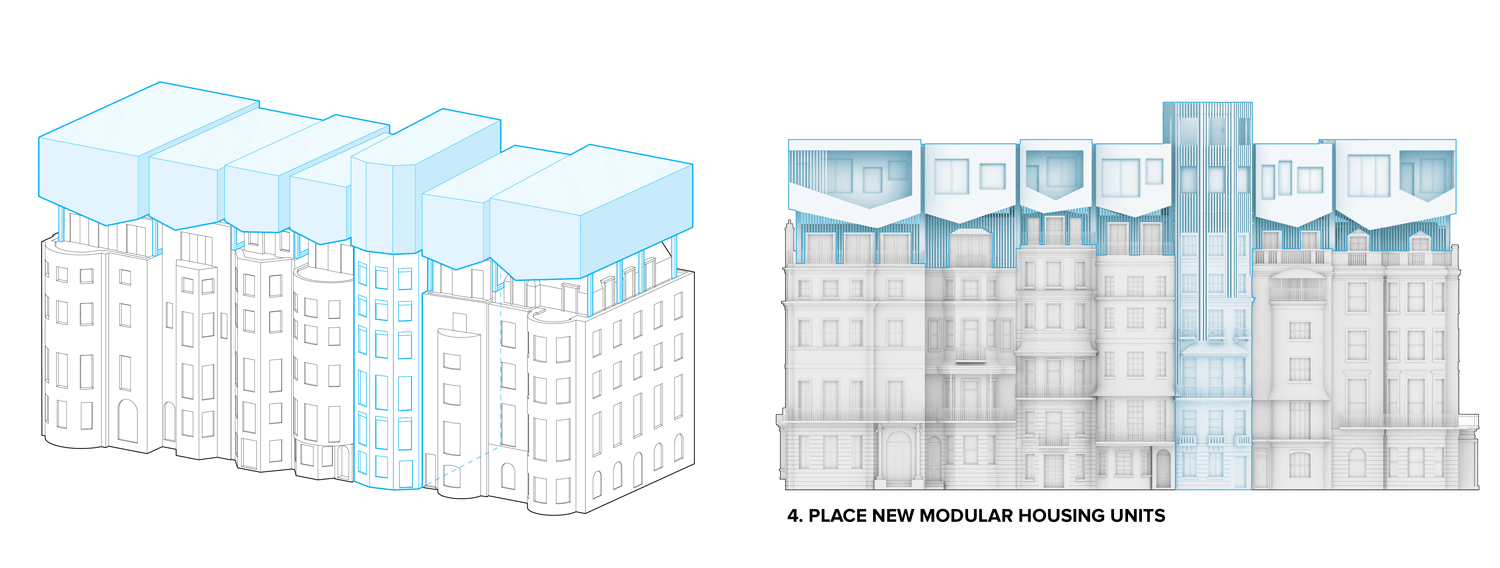
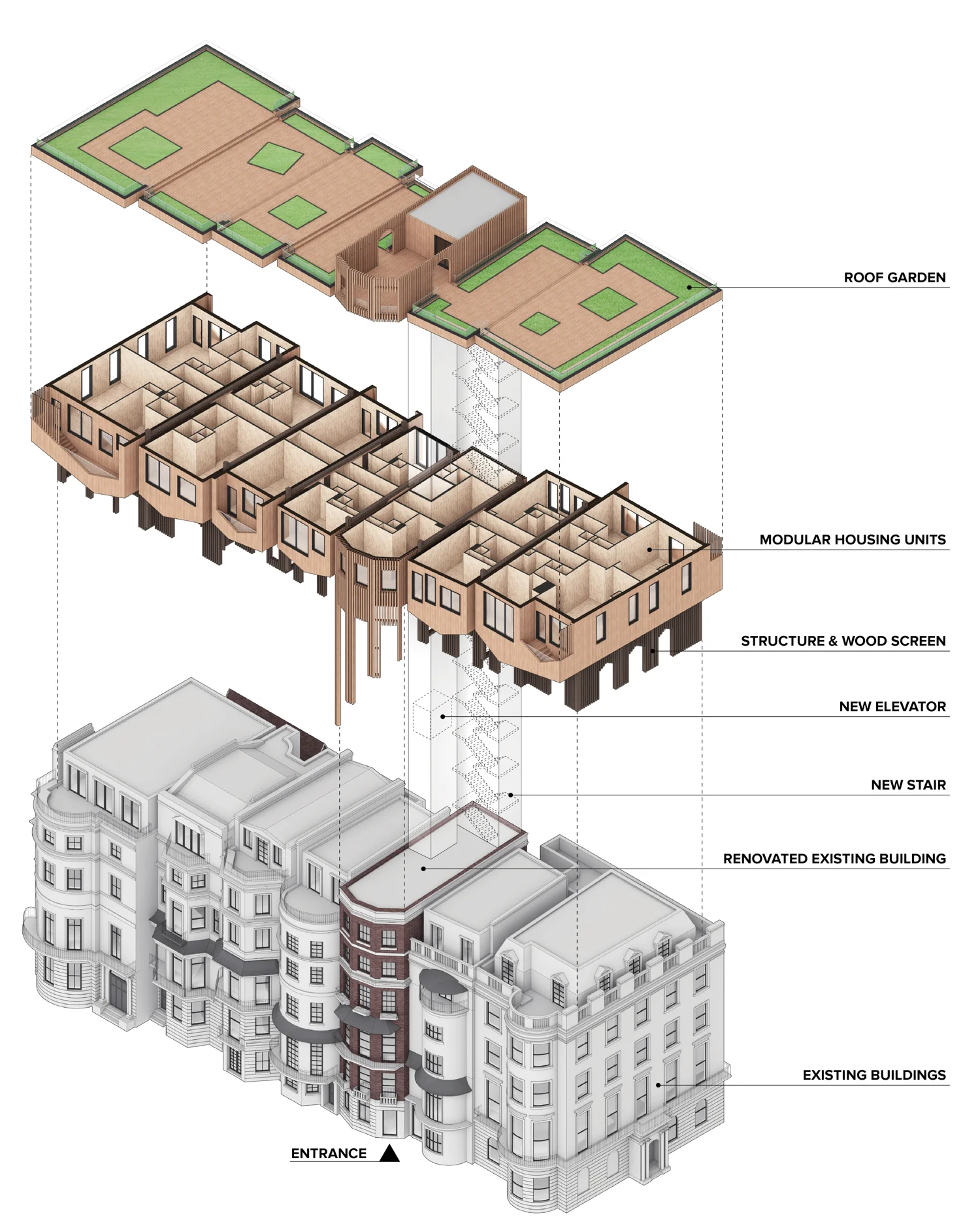
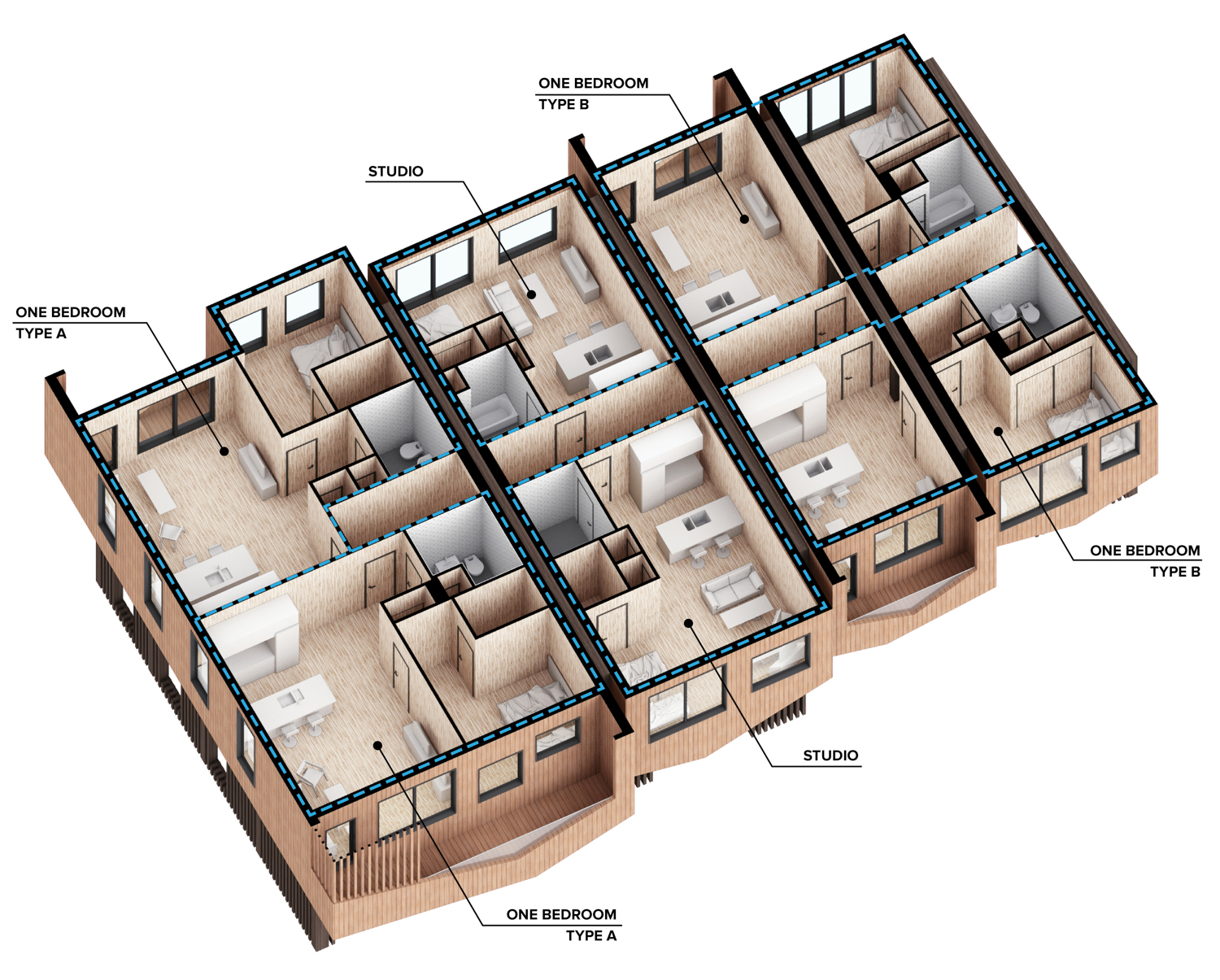
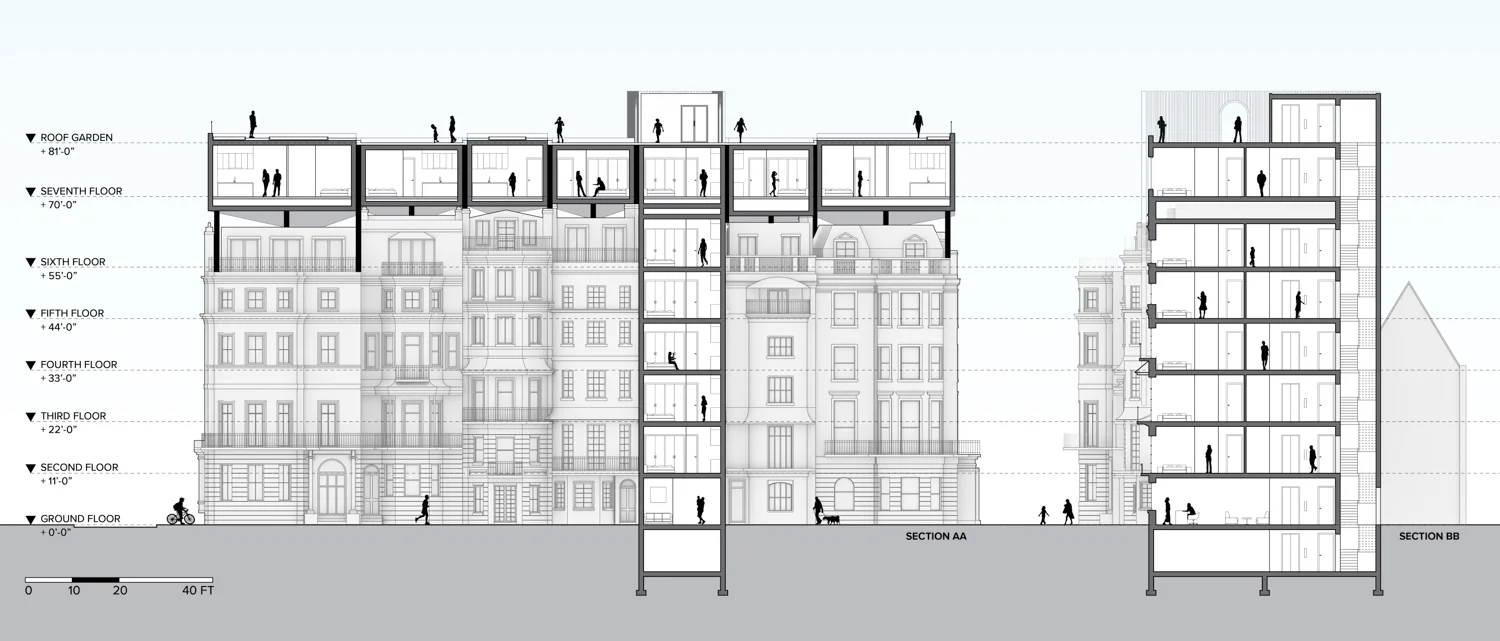
Flipped house is a new add-on housing typology that is incorporated with an existing row house. Basically, a flipped house is a modular system that uses the existing row house’s structure, which is embedded in the walls. The vertical timber structure of the existing building is extended beyond the roof by using a laminated veneer lumber (LVL), which is strong and lighter than a steel or concrete structure. The modular housing module will be located between extended LVL structures. Each housing module has two residential units and a corridor. Adjacent housing modules can be combined for a bigger unit. The cluster of housing modules forms a typical double-corridor residential floor. At the given site, flipped houses share only one existing building as a vertical circulation core. Renovating just one of seven existing buildings not only minimizes the destruction of historical features, but it also saves construction costs. In addition, this can maximize building efficiency by using a centralized MEP system in the core building.